Contents
Overview
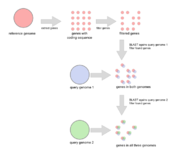
The Core Genome MLST (cgMLST) Target Definer extracts genes from one reference genome and uses BLAST to compare these genes against multiple query genome sequences on DNA level. Two sets of genes are defined, the cgMLST targets and Accessory targets.
Two tutorials are available for the cgMLST Target Definer:
Reference Genome
All gene annotations that also have a CDS annotation at the same location are used as initial reference genes. Therefore, the number of reference genes may slightly differ to the number in NCBI Genome Browser (e.g., tRNA will not be used in the cgMLST target definer).
cgMLST Targets
When the default filter settings are used, the cgMLST targets contain genes from the reference genome that
- are no homologous genes in reference genome
- do not greatly overlap each other in the reference genome
- contain one start and stop codon in the reference genome
- are found once in each of the query genomes (according to the thresholds)
- do contain correct number of stop codons in more than 80% of the query genomes
These targets are usually well suited for cgMLST typing.
Accessory Targets
Targets that are not included in the cgMLST targets because
- they are not found in each of the query genomes or
- they are found more than once in at least one query genome or
- they overlap in the reference genome or
- they do not contain correct number of stop codons in more than 80% of the query genomes
are added to the Accessory targets (with the default settings). These targets can be used to gain additional discriminatory power if typing using the cgMLST targets alone is not discriminatory enough.
Settings
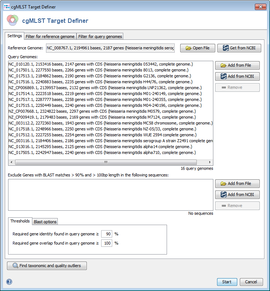
The cgMLST Target Definer panel allows to choose a reference genome and multiple query genomes. Filters and analyzers can be selected using the corresponding tabs.
Input files
A reference genome can be defined using a GenBank file or by download from NCBI Genomes using an accession number. Query genomes can either by defined by a GenBank or FASTA-file or by download using accession numbers. Multiple accession numbers for query genomes can be specified, separated by comma.
GenBank input
When reading GenBank files or downloading data from GenBank using an accession number, only the genes that have a CDS-region are used. Genes that are not continuous and genes with a codon start > 1 are skipped. The "locus_tag" is used as gene name.
FASTA input
If the FASTA file contains multiple sequences, all the bases are concatenated to one single sequence that is used as genome.
Exclude files
A list of files for exclusion of genes can be specified. Genes from the reference genome are excluded if a BLAST match with more than 90% similarity and > 100 bp length is found within the specified sequences. This feature is useful to exclude sequences from plasmids.
Filters
Genes are either discarded or moved to Accessory targets if they do not pass the filters. Two sets of filters exist:
- Filters for reference genome: these filters are only applied to the reference genome.
- Minimum Length Filter: Discard genes that are shorter than 50 bases.
- Start Codon Filter: Discard all genes that contain no start codon at the beginning of the gene.
- Stop Codon Filter: Discard all genes that contain no stop codon, more than 1 stop codon or if the stop codon is not at the end of the gene.
Note: Does not consider any GenBank annotations that indicate non-continuous coding regions. - Homologous Gene Filter: Discard all genes that have fragments that occur in multiple copies in a genome (with identity >= 90% and more than 100 bases overlap).
- Gene Overlap Filter: If two genes from reference genome overlap more than 4 bases, move the shorter gene to the Accessory targets.
- Filters for query genomes: these filters are applied to the genes found by BLAST in each query genome.
- Start Codon Filter: Moves all genes to Accessory targets that contain no start codon at the beginning of the gene in at least one query genome.
- Stop Codon Filter: Moves all genes to Accessory targets that contain no stop codon, more than 1 stop codon or if the stop codon is not at the end of the gene in at least one query genome.
Note: Does not consider any GenBank annotations that indicate non-continuous coding regions. This filter is disabled by default. - Stop Codon Percentage Filter: Move all genes to Accessory targets that fulfill the following condition in more than 80% of the query genomes:
the gene contains no stop codon, more than 1 stop codon or the stop codon is not at the end of the gene.
Taxonomic outliers
The button ![]() Find taxonomic and quality outliers can be used
Find taxonomic and quality outliers can be used
- to find taxonomic outliers in the query genomes or
- to find query genomes that contain many genes with erroneous stop codons, indicating a sequencing problem.
To find these outliers, all non-homologous genes from the reference genome are searched in each of the query genomes using BLAST. A list reports for every query genome how many of these genes were found and how many of the found reference genes contain stop codons.
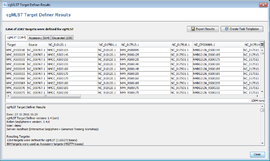
Result view
The result view lists all genes that are found as cgMLST targets or Accessory targets and all discarded genes.
The button ![]() Create Task Templates allows to create Task Templates directly from the results. The Task Template target names and sequences are imported from the reference genome.
Create Task Templates allows to create Task Templates directly from the results. The Task Template target names and sequences are imported from the reference genome.
Two Task Templates are created:
- The cgMLST Task Template contains all cgMLST targets.
- The Accessory Task Template contains all Accessory targets.
Target Definer Algorithm
The following pseudocode describes the algorithm:
Input: reference genome, query genomes, settings
extract reference genes (all features with a gene and a CDS entry) from reference genome filter reference genes, add filtered out genes to excluded list.
foreach query genome BLAST reference genes against query genome using settings foreach existing reference gene found BLAST hit for reference gene according to settings? no -> add to excluded list yes, multiple -> add to excluded list yes, single -> is it a known gene? yes -> add to found list for reference gene no -> create dummy gene and add it to found list for reference gene filter found genes, add filtered out genes to excluded list.
Output: reference genes and their found list (cgMLST targets), excluded list (filtered out genes)
Depending on the reason why they were filtered out, some of the filtered out genes are added to the Accessory targets (see filter description).