Contents
Overview
Local Single Linkage Clustering (SLC) IDs are assigned according to cgMLST profiles and can be defined for a project. The SLC ID can be used to detect and label clusters of samples with a similar allelic cgMLST profile automatically. Only samples of the specified project will be used for the clustering.
Defining cgMLST Local SLC IDs
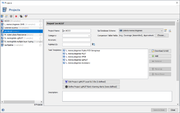
The local SLC IDs can be created and managed with the button in the project editor below the task templates section. The button is only enabled if a cgMLST task template was added to the project. The button icon is grey if no local SLC IDs are defined for the project yet, else it is colored blue.
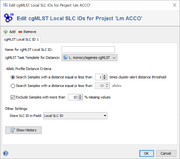
A cgMLST Local SLC ID definition contains the following settings:
- Name of cgMLST Local SLC ID
- A name that can be used as a reference for this definition. The name can be left empty if only one SLC ID is used.
- cgMLST Task Template for Distance
- If the projects contains multiple cgMLST Task Templates the one to be used for distance calculation can be selected here.
- Allelic Profile Distance Criteria
- Defines the allelic distance threshold for Local Single Linkage Clustering. By default, the cluster-alert threshold of the cgMLST Task Template is used. Alternatively a multiple of the cluster-alert threshold or an absolute allele distance can be chosen.
- By default all samples with more than 10% missing values will be excluded from clustering.
- Other Settings
- The database field can be selected here where the assigned SLC ID should be stored. By default it is stored in the field 'Local SLC ID' (in the section 'Epi Characteristic'). If multiple SLC IDs are defined for a project (e.g., hierarchical), the SLC IDs must be stored in different fields. Only the default field 'Local SLC ID' and/or newly created fields (must be contained in the 'Epi Characteristic' or a new section and must be of type 'Textfield') can be used to store SLC IDs. The fields that are used for storing the SLC IDs are automatically added to the comparison table default fields for this project.
When pushing the OK button the SLC ID definition is stored and active. At the same time all potentially existing SLC IDs of the project are written as Predefined ID in the history log.
![]() Hint: If a user has already own SLC IDs defined and wants the SLC IDs just automatically extended by the here described mechanism for new database samples and wants those predefined IDs logged in the history (see below), then the own IDs should be first imported into the SLC ID database field before storing a cgMLST Local SLC ID definition.
Hint: If a user has already own SLC IDs defined and wants the SLC IDs just automatically extended by the here described mechanism for new database samples and wants those predefined IDs logged in the history (see below), then the own IDs should be first imported into the SLC ID database field before storing a cgMLST Local SLC ID definition.
cgMLST Local SLC ID Assignment
If local SLC IDs are defined for the project, the clustering is automatically performed when a sample is processed in Pipeline Mode or the command Process Assembled Genome Data is used to process already assembled genomes. If a cluster is found, the SLC ID of the cluster is stored in the defined sample field (by default 'Local SLC ID' in section 'Epi Characteristic').
For each sample that is added to the project all stored samples of the same project are searched and found that have a similar allelic profile within the defined distance threshold:
- if no samples were found within the threshold, no SLC ID is assigned;
- else, if samples were found and all of them contain no SLC ID yet, a new ID is established and assigned to the new sample and to all found samples within the threshold;
- else, if samples were found and they contain all the same SLC ID (or no ID), the SLC ID is added to the new sample and to all found samples with ID assignment yet; and
- else, if samples were found and they contain different SLC IDs, a merging is performed. Thereby the SLC IDs are merged together and the merged SLC ID is assigned to the new sample, to all found samples within the threshold, and to all stored samples of the project that had one of the merged SLC IDs assigned. The new ID is created by concatenating all merged IDs with the delimiter "/".
The SLC IDs are only assigned to samples that were found in the search and not to samples that are similar to the found ones. Therefore, when a new local SLC ID is defined for a project that contains already samples, it is recommend to perform immediately after finishing the definition a cgMLST Local SLC ID assignment for the existing samples (see below).
![]() Important: The field that was chosen for storing the SLC IDs can be edited manually. However, due to merging, it can happen that the field value is exchanged by SeqSphere with a merged SLC ID.
Important: The field that was chosen for storing the SLC IDs can be edited manually. However, due to merging, it can happen that the field value is exchanged by SeqSphere with a merged SLC ID.
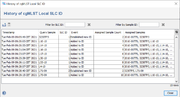
History of cgMLST Local SLC ID Assignments
The button "Show History" in the editor panel of the Local SLC ID definition can be used to list the history of all SLC ID assignments in a table. By default the table is sorted according to the time stamp of creation (newest entry on bottom). Selecting row(s) of the table, right-clicking, and selecting the command opens a comparison table with all involved samples. The table rows can be filtered by entering either a local SLC ID or a sample ID. SLC IDs entered/edited manually or imported after storing a new Local SLC ID definition are not logged in the history. Only SLC IDs already existing when defining and storing a new Local SLC ID mechanism are logged in the history.
Perform cgMLST Local SLC ID Assignment for Existing Samples
The button ![]() in the toolbar of the project manger window allows to perform for the selected project a local SLC ID assignment for existing samples. If multiple SLC IDs definitions are defined for this project then select in the upcoming dialog first the definition for which all the following should apply. The option Remove potentially existing cgMLST IDs and reset ID counter to 1 is selected by default. If this option is used all potentially existing history logs and SLC ID field entries are deleted (usually this field should be empty anyway; however a user could have entered manually or imported field values) and a single linkage clustering of all project samples is initiated with the ID counter starting to count from 1. SLC IDs are merged and the lower ID, i.e. earlier ID, is used as ID for the merged samples.
in the toolbar of the project manger window allows to perform for the selected project a local SLC ID assignment for existing samples. If multiple SLC IDs definitions are defined for this project then select in the upcoming dialog first the definition for which all the following should apply. The option Remove potentially existing cgMLST IDs and reset ID counter to 1 is selected by default. If this option is used all potentially existing history logs and SLC ID field entries are deleted (usually this field should be empty anyway; however a user could have entered manually or imported field values) and a single linkage clustering of all project samples is initiated with the ID counter starting to count from 1. SLC IDs are merged and the lower ID, i.e. earlier ID, is used as ID for the merged samples.
If the option Remove potentially existing cgMLST IDs and reset ID counter to 1 is deselected the SLC ID field entries are not removed and instead used for ID assignment. If a new ID number must be assigned the counter starts assigning ID numbers with a value one integer higher then the highest already existing ID number. Furthermore, when doing a merging a concatenated name built from all involved IDs is used.
Searching And Analyzing Samples With (potentially) Identical Local SLC IDs
If a Sample is loaded it is possible to search (recursively) for a given threshold samples similar by cgMLST profile via the command Search Similar Samples in Database. In a default similarity search only samples are found, that are within the defined allelic threshold compared to the query sample. If the recursive option is turned on, all samples that are within the defined allelic threshold to any other found samples are returned. This search is repeated until no additional samples are found. Similar the command Tools | Search Similar Samples in Database can be elicit from the main menu to find potentially matching samples once query sample(s) are selected.
If samples are opened in a Comparison Table and sample(s) are selected, again a (recursive) similarity search for those samples can be conducted via the Search Similar Samples in Database command. If the SLC ID(s) of interest are stored in the database field Local SLC ID it is possible via the command Add Additional Samples with Same SLC ID to load in the comparison table immediatelyall stored samples of the project with identical SLC ID(s). If the SLC ID(s) of interest are stored in a different database field, the Add Additional Samples by Metadata Search command must be used. Next, the database field that holds the SLC IDs must be selected, the SLC ID(s) values of interest must be entered, and finally the search must be conducted.