Contents
1 Overview
This tutorial describes how to use the Ridom Typer software to analyze single target Sanger sequence data (e.g., chromatogram files) using a predefined 16S rDNA reference library. The results are interpreted according to the CLSI MM18 guidelines. This document states that amplicons and sequences should be at least 450 base pairs (bp) in length. The most common broad-range DNA target to identify bacteria is the first 500 bp of the 16S rRNA gene that cover especially the highly variable V3 and V4 regions. Therefore, using 5'-16S rDNA universal eubacterial primers like 27f (5'-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG) and 519r (5'-GWATTACCGCGGCKGCTG) for amplification and sequencing covering this stretch is highly recommended.
2 Preliminaries
- This tutorial requires a running Ridom Typer client and server, version 11.1 or newer. Start the Ridom Typer server, and then launch the Ridom Typer client and initialize the database. For evaluation purposes, a free evaluation license can be requested.
- This tutorial uses a 16S rDNA task template that is not available via the Task Template Sphere. Therefore, you must download the 16S rDNA LTP task template manually. Instructions for importing it are provided later in the tutorial. The task template is based on the All-Species Living Tree Project (LTP).
- Citation: Ludwig W, Viver T, Westram R, Francisco Gago J, Bustos-Caparros E, Knittel K, Amann R, and Rossello-Mora R. Release LTP_12_2020, featuring a new ARB alignment and improved 16S rRNA tree for prokaryotic type strains. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2021, 44: 126218 [PubMed 34111737]
- Download and extract the example data archive Ridom_Typer_Examples_Sanger_16S.zip
3 Downloading Task Template and Creating Project
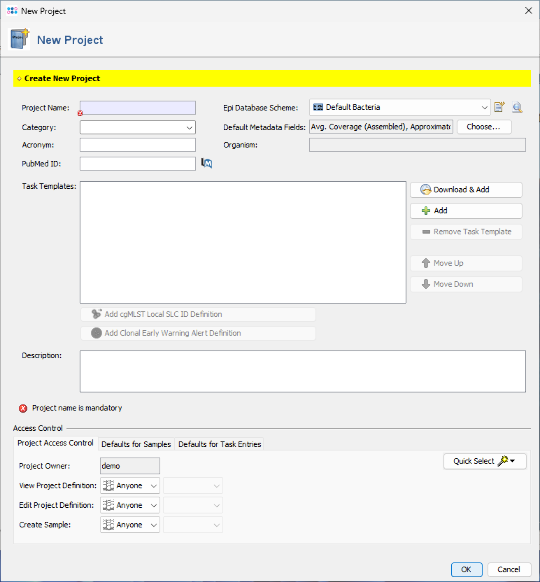
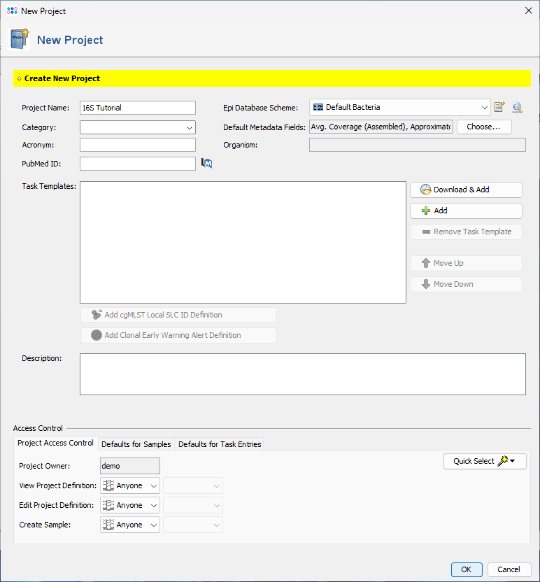
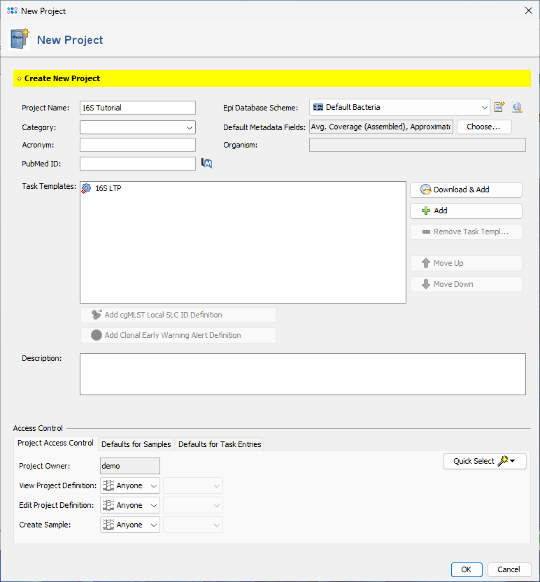
- Step 1: Create a new Project for your sample data using the menu command File | New | Create Project
- Step 2: Enter a name in the Project Name field (e.g., 16S Tutorial ). All other fields can be left at their default values.
- Step 3: Click
 Add in the Task Templates section to add a task template to the project. The Add Task Template to Project dialog opens, showing task templates already available in the database. Click
Add in the Task Templates section to add a task template to the project. The Add Task Template to Project dialog opens, showing task templates already available in the database. Click  Import from File, and select the downloaded task template file 16S_rDNA_LTP.tasktemplate
Import from File, and select the downloaded task template file 16S_rDNA_LTP.tasktemplate
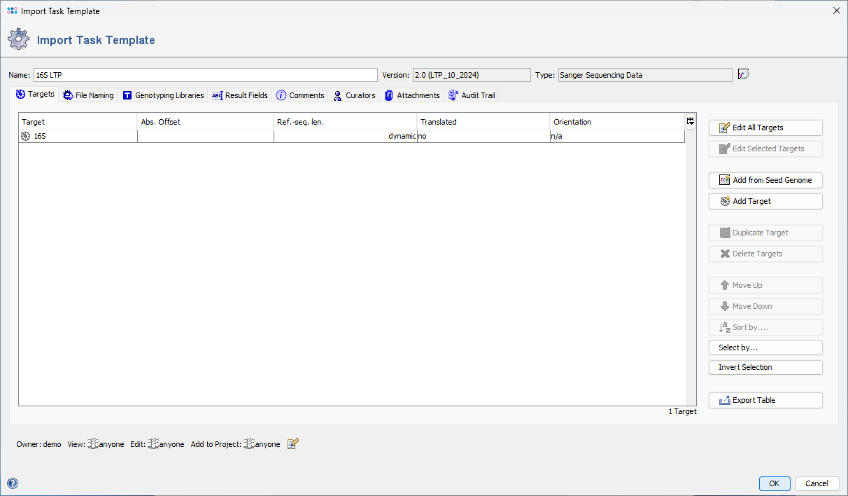
- Step 4: An editor window opens, displaying the 16S rDNA LTP task template to be imported. No further editing is required for this tutorial. Click OK to confirm the dialog and import the task template. The newly imported template will be automatically selected in the Task Templates window. Click OK again to confirm the dialog.
- Step 5: The imported task template has been added to the project. Click OK to confirm and save the new project.
- Ridom Typer is a resequencing software. Once you have setup a project like this you can literally analyze hundreds/thousands of sequence data.
4 Assembling and Analyzing Sanger Sequence Data
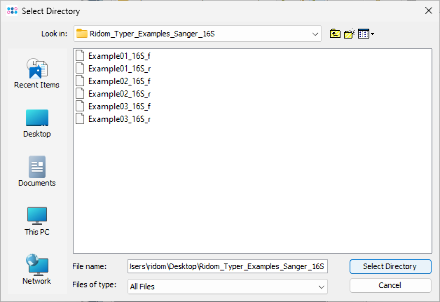
- Step 1: Select File | Process Sanger Sequencing Data from the menu. Then, click
 button above the file browser panel on the left and choose the directory where you extracted the downloaded tutorial example data.
button above the file browser panel on the left and choose the directory where you extracted the downloaded tutorial example data.
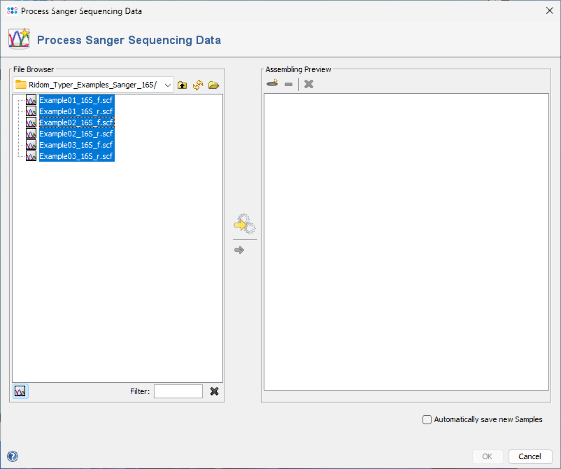
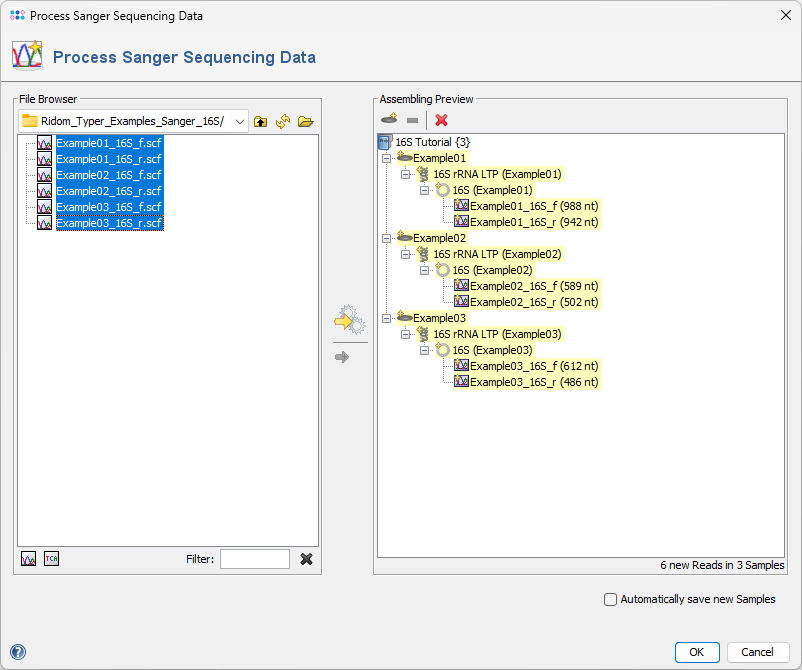
- Step 2: The files are now displayed in the file browser panel on the left. Select all six files (e.g., with CTRL-A).
- Step 3: Now click the button
 in the toolbar in the center of the dialog.
in the toolbar in the center of the dialog.
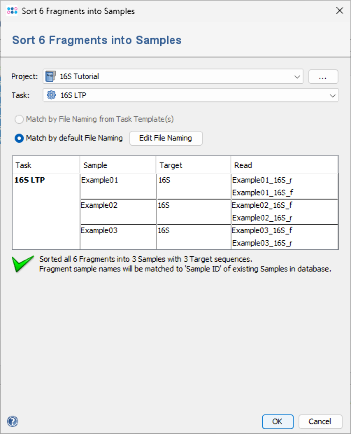
- Step 4: A dialog will appear to sort the chromatograms (fragments) into Samples. Make sure the correct 16S project is selected. Choose Match by default File Naming. Since the file naming is automatically recognized, the six chromatograms will be sorted into three different samples. If this does not work with your own data later, click the Edit File Naming button to adjust the settings (alternatively, file naming can be defined in the task template). Finally, confirm the dialog by clicking OK.
- Step 5: The preview on the right displays the six chromatograms sorted into the three newly defined Samples. Click OK to confirm the dialog and begin assembling the chromatograms and processing the Samples.
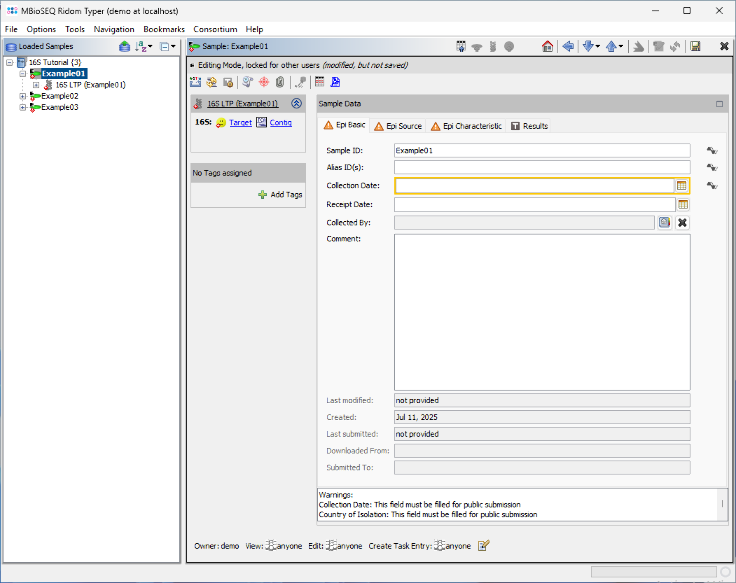
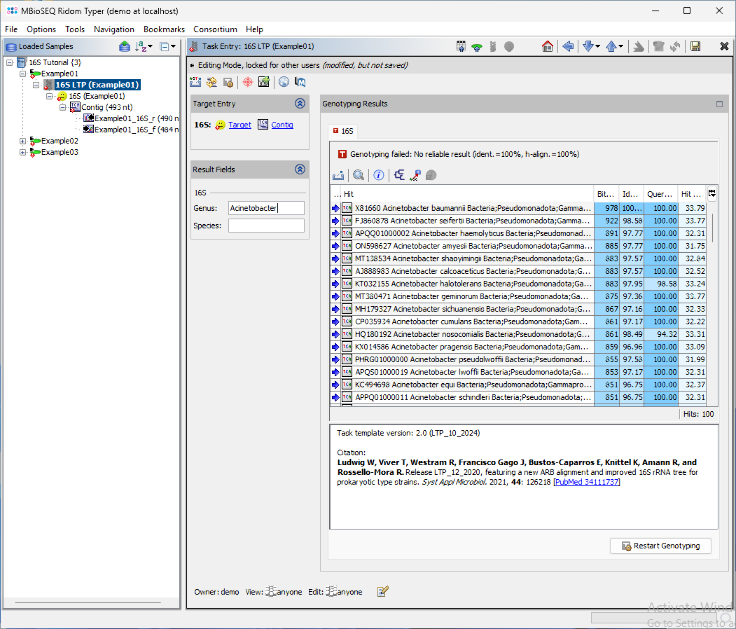
- Step 6: After a short moment, the reads are assembled, and the three new Samples will appear in the navigation tree on the left of the main window. On the right, an overview and the epi metadata for the first Sample are displayed. For the processed 16S target, links to the Target and Contig will be shown. Click the Contig link to view the assembled sequence data.
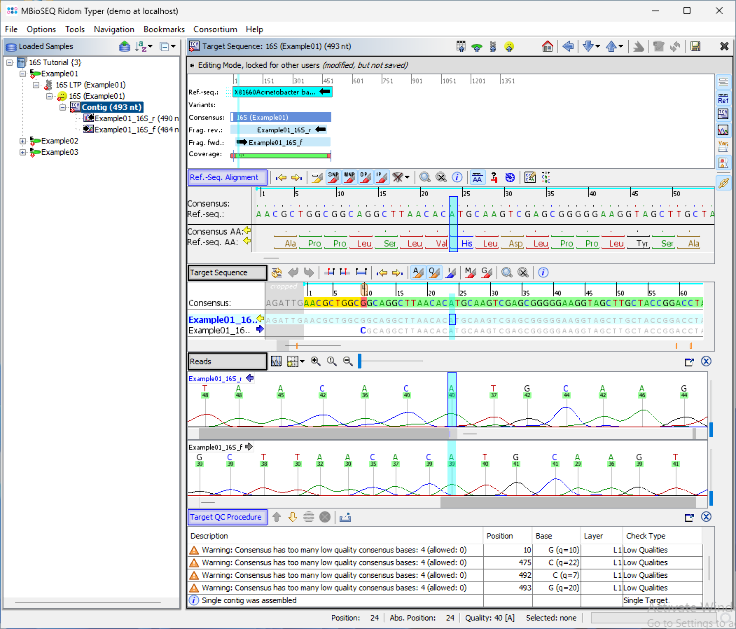
- Step 7: The assembled chromatograms and the contig alignment with the best matching reference sequence from the 16S library are displayed. Clicking on the position in the Target Sequence section highlights the corresponding base calls in the chromatogram. If needed, base call errors can be edited manually by right-clicking into the chromatograms. This is not required for this tutorial sequence data.
- For use with further web services (e.g., NCBI Blast search), the consensus can be exported to the clipboard or to a FASTA file by right-clicking on the consensus in the Target Sequence section and choosing Copy Bases of Consensus Area(s) to Clipboard or Export Bases of Consensus Area(s) to File.
- In the navigation tree on the right of the window now double-click on the subnode 16S rDNA LTP of the first sample to show the result of the 16S task.
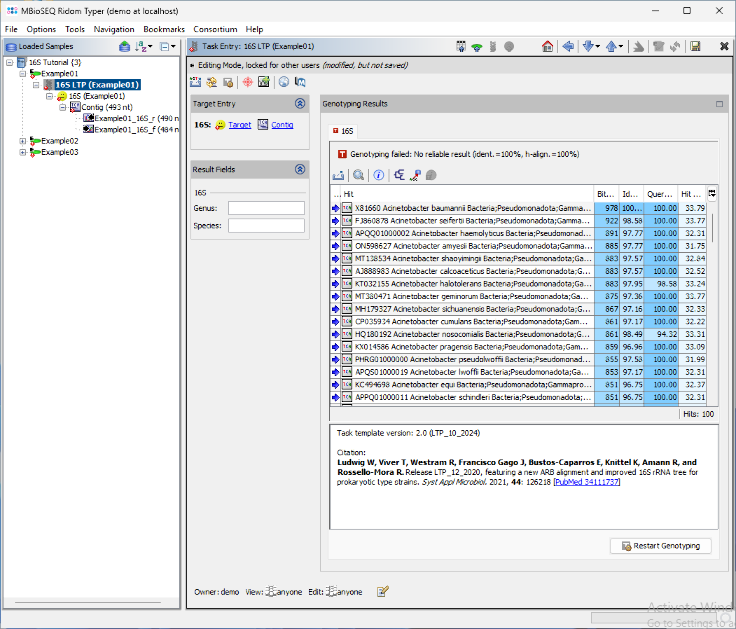
- Step 8: The BLAST search results are displayed in a table. The top match Acinetobacter baumannii is highlighted in green, as it meets the required thresholds. The match is longer than 450nt, with an identity above 99.0%, and the next closest match has more than 0.8% distance. As a result, the Genus and Species fields are automatically populated. Additionally, a brief report text describing the typing result is stored in the Comment field. Next, open the 16S rDNA LTP task for the other two samples by double-clicking the corresponding nodes in navigation tree on the left.
- Step 9: For the two other samples, the top entry in the BLAST result table is highlighted yellow because only the genus level can be determined from this result. The comment section will shows the potential species.
- The result reporting algorithm is based on CLSI MM18 Interpretive Criteria for Identification of Bacteria and Fungi by Targeted DNA Sequencing (2nd edition). For most bacteria the following blast match thresholds are used: match length ≥ 450nt; species match identity ≥ 99.0%; species match separation > 0.8%; genus match identity ≥ 97.0%. Different thresholds are used for Mycobacteria (species match identity = 100.0%; species match separation > 0.4%; genus match identity ≥ 99.0%) and for the aerobic actinomycetes Nocardia, Gordonia, Streptomyces, Rhodococcus, Actinomadura, Tsukamurella (species match identity ≥ 99.6%; species match separation > 0.4%; genus match identity ≥ 99.0%).
5 Storing and Retrieving Samples
- Step 1: Choose File | Save All from the menu
 to store the samples in the database on your Ridom Typer server. Then select File | Close All to remove them from the workspace.
to store the samples in the database on your Ridom Typer server. Then select File | Close All to remove them from the workspace.
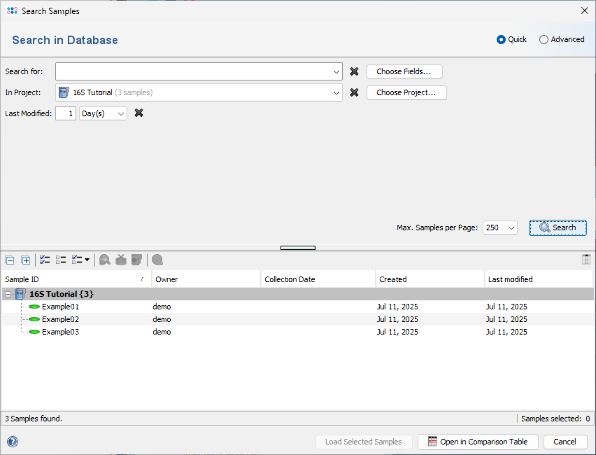
- Step 2: Choose
 File | Search Samples. In the Project box, select the desired project, and set Recently modified to 1 day(s). Then click the Search button.
File | Search Samples. In the Project box, select the desired project, and set Recently modified to 1 day(s). Then click the Search button.
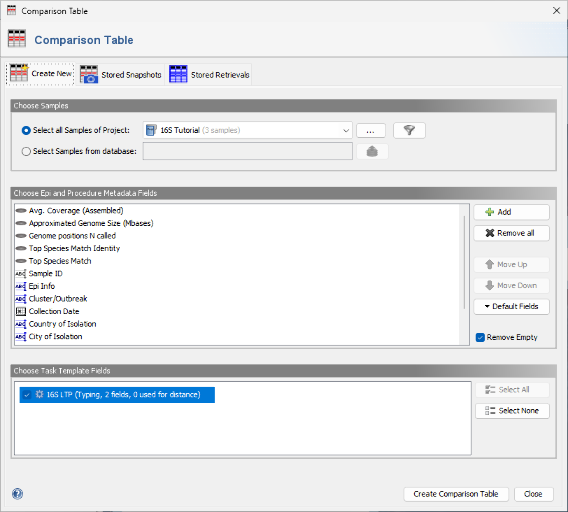
- Step 4: The Samples that were just saved are listed in the search results and can be reloaded into the workspace. For now, close this dialog, and select Tools | Comparison Table from the menu.
- Step 5: The new 16S project and the 16S rDNA LTP task are pre-selected by default. Confirm the dialog by clicking the Create Comparison Table button.
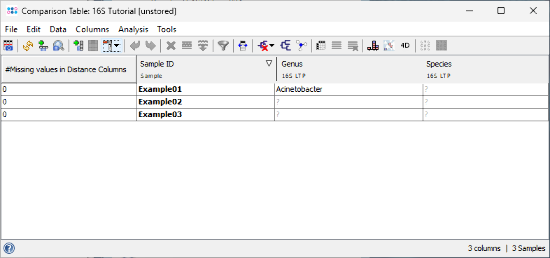
- Step 6: A comparison table is displayed for the three samples. The fields Genus, Species, and Comment show the results of the 16S rDNA LTP task.
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR USE IN CLINICAL DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES.