Microbial genomics software for clonal and plasmid transmission studies and real-time surveillanceMBioSEQ Ridom Typer software - formerly known as SeqSphere - is designed for distributed work-groups (client/server model) and allows automatic processing and analyzing of NGS (e.g., Illumina, Ion Torrent, Pacific Biosciences [PacBio], or Oxford Nanopore Technologies [ONT]) and Sanger sequence data. Ridom Typer is the single solution for easy and automated whole genome microbial typing that empowers your laboratory for smarter decisions (Nat Biotechnol. 2013,31:1148). No scripting or bioinformatics skills requiredMBioSEQ Ridom Typer includes every tool that is needed to do bacterial typing with whole genome sequencing (WGS) data. The software works directly with the short- or ONT long-read FASTQ files produced by a NGS sequencer. A pipeline mode allows to import, assemble and analyze hundreds of read files without any user intervention. cgMLST schemes for cluster analysis can be downloaded from the public cgMLST.org nomenclature server. Elevate your microbial research to the next levelA variety of methods have been developed to generate isolate-specific fingerprints for genotyping. However, until recently there was no single typing method available to address all bacterial species, different population structures (monomorphic vs. panmictic), and all study types (e.g., evolutionary/phylogenetic, population genetics, or transmission chain/outbreak). For decades, the common typing method was based on multi locus sequence typing (MLST) of 5-7 housekeeping genes or pulse field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). However, these methods either lack discriminatory power or are labor intensive and difficult to standardize. Now, microbiologists everywhere can experience the genomic revolution that benchtop next generation sequencing (NGS) provides. With fast and affordable microbial WGS and automatized software analysis, microbiologists can use genome-wide gene-by-gene allele calling of hundreds/thousands of genes (core genome MLST [cgMLST]) for genotyping. cgMLST schemes consist of a fixed set of conserved genome-wide genes. Alleles are used instead of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) or concatenated sequences to mitigate the effects of recombination and to enable for a global and public nomenclature. The high discriminatory power of cgMLST, coupled with rapid and simple WGS workflow, makes this complete solution ideal for everyday usage in a laboratory, e.g., for prospective surveillance of multi-drug-resistant bacteria in a hospital ( JCM 54: 2874, 2016 [Illumina] and JCM 63: e0012125, 2025 [PacBio]). That is, one disruptive, accurate, and highly reproducible genomic technology ( JCM 55: 908, 2017 ) that fits any bacteria or virus (SARS-COV-2), any research topic, and any lab is finally within reach for every microbiologist. |
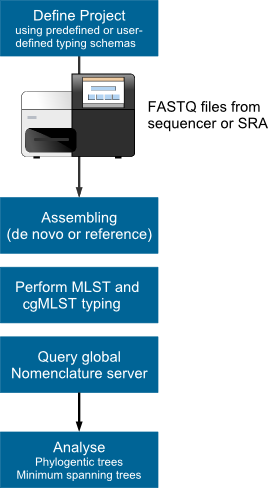 Figure. Microbial WGS next generation sequencing and genome-wide gene by gene (cgMLST) analysis workflow. |
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR USE IN CLINICAL DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES.




