Contents
Introduction
Here we compare the effect of Medaka (v1.12 and v2.0) polishing and the ONT-cgMLST-Polisher on cgMLST errors.
Methods
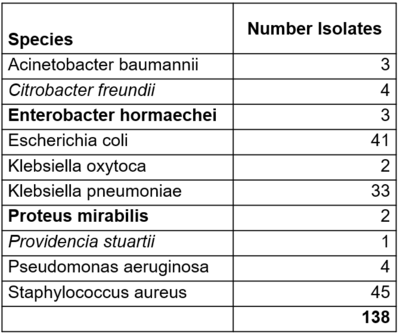
We used published short-read (Illumina NextSeq 550) and long-read (ONT, Rapid Barcoding Kit-24-V14, R10.4.1) sequencing data of multidrug-resistant bacteria (Landman et al.). From the initially 356 MDROs, we excluded species with less than three isolates (n=10), isolates with a wrong species match (n=1) or evidence for high contamination (n=1) and isolates where the ONT coverage was below 50x (NO-MISS recommendation) (n=206) leading to an evaluation dataset of 138 isolates.
Table: Number of isolates per species. In bold new public cgMLST schemes and in italics non-public new stable schemes.
Illumina reads were downsampled to a coverage of 100x and assembled with SKESA v2.3.0. For ONT, reads were basecalled with Dorado v0.3.2 --duplex mode SUP dna_r10.4.1_e8.2_ 400bps_sup@2023-09-22_bacterial -methylation (AKA ‘Rerio’; now included in m4.3). Afterwards, the reads were trimmed for quality 10 and a minimum length of 500 with Chopper v0.7.0, downsampled to 100x coverage with Rasusa v0.8.0 --deterministic , and de novo assembled with Flye v 2.9.3-b1797 --nano-hq --deterministic.
The resulting Flye assemblies were then either left as is or polished with Medaka v1.12 (SUP m4.3 model) or Medaka v2.0 (bacterial methylation model). The ONT-cgMLST-Polisher was run over all three assemblies.
Ground-truth references were constructed using Hybracter v0.10.0 hybrid assemblies.
ONT-cgMLST-Polisher Accuracy Results
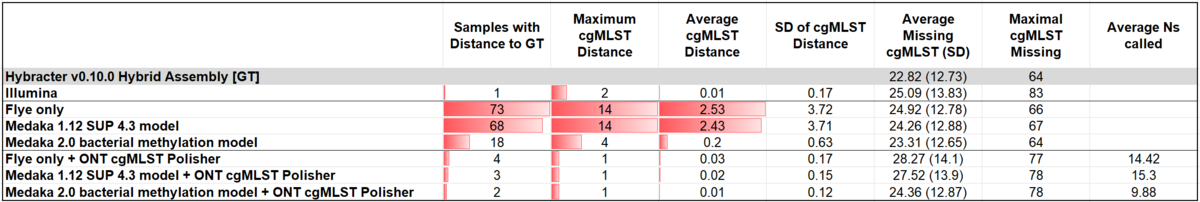
Table: Summary statistics of cgMLST distances between different assembly/polishing approaches and a "ground-truth" (Hybracter v0.10.0 hybrid assembly). Ns counted in all chromosomal contigs.
Using Hybracter v0.10.0 hybrid assemblies as the ground-truth, the cgMLST allelic distances of the different assemblies to their respective ground-truth were assessed and summarized over the dataset.
Medaka v2.0 already reduced the number of samples with a distance to the ground-truth and the average distance substantially in comparison to Flye-only and Medaka v1.12. Polishing with the ONT-cgMLST-Polisher further enhanced the accuracy, leaving only 2 out of 138 samples with a distance to the ground-truth.
ONT Priority AMR Target Recovery and Location Results
In addition to cgMLST distances, we searched the Illumina and the ONT Medaka v2.0 assembly (without ONT-cgMLST-Polisher) for priority AMR targets (targets that might confer resistance to carbapenem, colistin, vancomycin, or methicilin or that contain ESBL or AmpC in their name) and compared their location (chromosomal or plasmid-borne) as predicted by MOB-recon with the respective location in the ground-truth. In comparison, Illumina had more missing and also more misplaced targets than the ONT sequenced data.
Table: Number of priority AMR targets found in the 138 samples and their placement in respect to the ground-truth.
Conclusion
Version 2 of Medaka improves ONT sequencing accuracy substantially. The ONT-cgMLST-Polisher further improves the error rate and facilitates reliable genotyping. Further, AMR target recovery and placement is more reliable with ONT than with Illumina data.
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR USE IN CLINICAL DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES.