| wiki | search |
Contents |
Preparation
- Define a Task Template for whole genome sequencing data
- Be sure to add the Task Template to a Project
- When working with short reads, use the Velvet de nove assembler or the BWA read mapper to assemble the reads into one or more contigs.
Choose Input Files
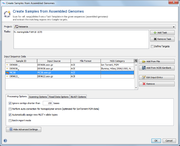
Use the menu function ![]() File | Create Samples from Assembled Genomes to open a dialog window.
File | Create Samples from Assembled Genomes to open a dialog window.
A Project and at least one Task Template must be selected. If a single Task Template is selected, the process can be limited to specific targets using the Define Targets checkbox.
In the Input Sequence Data section the files with whole genome sequence data can be selected. It is possible to either add files using the ![]() Add from file-button or to add sequences from NCBI GenBank using the
Add from file-button or to add sequences from NCBI GenBank using the ![]() Add from NCBI GenBank button.
Add from NCBI GenBank button.
Allowed input file formats are FASTA, GenBank, SAM/BAM and ACE-files.
To modify the name of the created Sample
- double-click the Sample-ID column or
- select the row in the table and press the button
 Edit Properties.
Edit Properties.
If the Sample-ID column contains the name of an existing Sample, the contigs will be added to this Sample.
Press the button Show Advanced Settings to show additional parameters:
- Processing Options
- Ignore contigs shorter than: This setting is used to improve the speed by ignoring contigs in the input file that are shorter than a minimum length (default: 200bp).
- Perform auto-correction for homopolymer errors: This feature allows to automatically correct some of the errors in NGS data from IonTorrent PGM.
- Assign new allele types for local typings: Only applicable if a Task Template defines an Allele typing query. The allele types are automatically queried, and if possible a new allele type is assigned to unknown allele sequences.
- Automatically assign or submit new allele types: Only applicable if a Task Template defines an Allele typing that is linked to the Ridom nomenclature server. The allele types are automatically queried from the nomenclature server. If unknown allele types are found, the Sample is submitted to the nomenclature server and new allele types are assigned. This requires that the mandatory data (Country of isolation, Isolation date) were imported into the Samples previously.
- Batch import mode: If this setting is enabled, the scanning of genes and storing Samples is performed without any user interaction. By default only empty targets in existing Samples are filled in batch mode. By selecting Overwrite existing targets also already filled targets are overwritten.
- Read Data Options: The read alignment can be imported from ACE- and SAM/BAM-files.
- Import read data for targets with failed analysis only: The read alignment data of targets where the analysis failed (yellow icon) will be kept. Alignment data of other targets will be discarded if not configured by other settings.
- Import read data for all targets: The read alignment data of targets will be kept.
- Scanning Options: Either use the thresholds that are defined by the Task Template(s) or manually define thresholds that should be used for ref.-seq. scanning.
- BLAST Options: The parameters that are used for BLAST when performing the ref.-seq. scanning. Default parameters are word size 11, mismatch penalty -1, match reward 1, gap open costs 5 and gap extension costs 2.
Click OK to start the "Create Samples from Genome Sequences" process.
Preview the Results
During this process, the reference sequences of the selected Task Templates are searched in the input data (using BLAST). If one and only one hit is found, that fulfills the defined thresholds, this is taken as the correct position of the target in the input data.
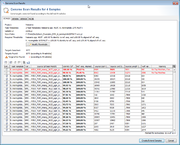
When this process has finished in non-batch mode, a table with all found hits is shown per input data file. Each row in this table represents one target that was searched. The rows that are highlighted red do not fulfill the defined thresholds.
Rows for targets that already exist in a Sample with the same name are disabled. To enable overwriting of existing target sequences, mark the checkbox Allow to replace existing targets.
The first column of the table shows a checkbox that defines if the found region should be extracted as sequence for the searched target. By default only the targets that fulfill thresholds unambiguously, and that are not already found in an existing Sample are selected.
The thresholds can be changed in this preview. The selection marks in the first column are updated automatically. The selection marks can also be changed manually row by row.
Press the confirm button at the bottom of the window to create the new Samples, or to extend existing ones.
Import the Results
Now the regions that match to the target reference sequence are extracted from the input data, and added to new or existing Samples. If the input data contains the read information (ACE file), the aligned reads for this are also extracted and imported corresponding to the advanced settings.
SAM/BAM files
For SAM/BAM files (they contain reference-mapped data) a special consensus caller is used.
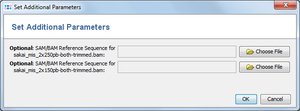
If SAM/BAM files do not contain a reference sequence, a dialog windows opens that allows to specify a FASTA-file with the reference sequence. The sequence names in the FASTA-file must match the names in the SAM/BAM file.
Reads with a mapping quality below a given threshold (default 10) are discarded when the SAM/BAM file is read. The threshold can be set in the Preferences.